Introduction: Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors and the BCL-2 antagonist venetoclax have significantly improved the outcome of CLL patients, including patients with high risk CLL who had dismal outcome with chemo-immunotherapies. Nonetheless, CLL patients with 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutations may continue to have an increased risk for treatment failure with BTK inhibitors or venetoclax when compared to CLL patients with lower-risk disease. For example, the median progression free survival (PFS) of ibrutinib-treated relapsed and refractory CLL patients in the PCYC-1102 study was 52 months for the entire population, but only 26 months for those with 17p deletion. In a phase-2 study of ibrutinib in CLL patients with 17p deletion/TP53 mutations (NCT01500733) it was noted that the 5-year PFS was 19% for relapsed and refractory patients, but 74% in treatment-naïve CLL patients, indicating that remission duration is substantially longer in patients with 17p deletion/TP53 mutation when ibrutinib is used in the frontline disease setting. Here, we reviewed the long-term outcome of treatment -naïve CLL patients with 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutation receiving ibrutinib, alone or in combination with rituximab on an investigator-initiated Phase-2 trial (NCT02007044).
Patients: 27 treatment-naïve CLL patients with 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutation received ibrutinib, alone (n=15) or in combination with rituximab (n=12). Responses were evaluated according to the 2008 iwCLL criteria, with the exception that lymphocytosis was not the sole criterion for disease progression. PFS was defined as the time from start of treatment to progression, death or last follow-up.
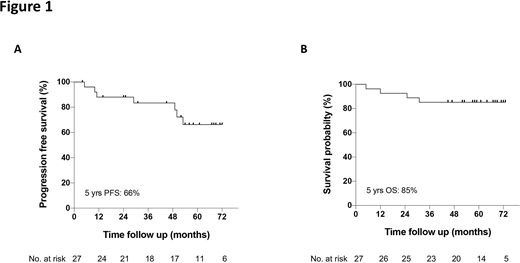
Results: The median age was 62 years, 67% were male, 78% had unmutated IGHV, and 33% advanced stage disease (Rai stage III-IV). After a median follow-up of 61 months, median progression free and overall survival were not reached, and the estimated 5-year progression free and overall survival were 66% and 85%, respectively (Figure). This is markedly better than the published 5-year PFS of 15.3% in 17p deleted CLL patients after fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab (FCR). Most common reason for treatment discontinuation was disease progression, which occurred in 6 patients (22%), with a median time to progression of 39 months (range, 10 - 53 months). Objective responses were noted in all except one patient (overall response rate 96%), with complete remissions in 10 patients (37%), and partial remissions in 16 patients (59%). Median levels of CLL bone marrow infiltration declined from 76% at baseline, to 26% after 12 months, and 14% after 24 months of therapy. Remission duration was not different in patients achieving complete or partial remissions, suggesting that deep remissions are not a prerequisite for durable remissions. Venetoclax-based therapy, which generally induces deeper remissions, does not seem to induce more durable remissions (2-year PFS 74% with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab in treatment-naïve CLL with 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutation), although cross-trial comparisons are problematic, especially given that venetoclax was administered as a fixed-duration regimen. Future research will determine if combination therapy results in a further survival improvement.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that frontline therapy with ibrutinib results in long-term remissions in high-risk CLL patients with 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutations, despite the lack of deep remissions, with an estimated 5-year PFS of 66%.
Jain:Aprea Therapeutics: Research Funding; Verastem: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Precision Bioscienes: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BeiGene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Fate Therapeutics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding. Kadia:Ascentage: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pulmotec: Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Cyclacel: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Cellenkos: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; JAZZ: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding. Andreeff:Centre for Drug Research & Development; Cancer UK; NCI-CTEP; German Research Council; Leukemia Lymphoma Foundation (LLS); NCI-RDCRN (Rare Disease Clin Network); CLL Founcdation; BioLineRx; SentiBio; Aptose Biosciences, Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi-Sankyo; Jazz Pharmaceuticals; Celgene; Amgen; AstraZeneca; 6 Dimensions Capital: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo; Breast Cancer Research Foundation; CPRIT; NIH/NCI; Amgen; AstraZeneca: Research Funding. Thompson:AbbVie: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy; Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria. Kantarjian:Janssen: Honoraria; Oxford Biomedical: Honoraria; Actinium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive biotechnologies: Honoraria; Aptitute Health: Honoraria; Ascentage: Research Funding; BioAscend: Honoraria; Delta Fly: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Jazz: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding. O'Brien:Eisai: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Regeneron: Research Funding; KITE: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy; Vida Ventures: Consultancy; Janssen Oncology: Consultancy; Vaniam Group LL: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Sunesis: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy; Acerta: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Verastem: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Aptose Biosciences: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy. Burger:Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Beigene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal